Managing Supply Chain Risks
The goal of Supply Chain Risk Management (SCRM) is to ensure continuity of production processes. To this end, companies and their supply chains must be prepared for, and protected against, unexpected events (proactive SC risk management). However, companies cannot counter all risk and must be able to deal effectively with the impacts from supply chain disruptions (reactive SC risk management).
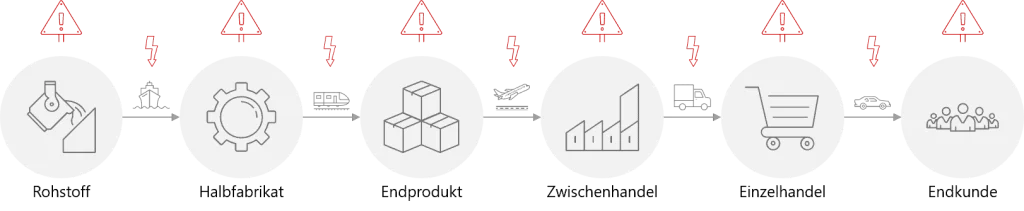
Due to the level of complexity in modern supply chains parts of your chain, which typically recieve little attention, can end up being the source of wide spread disruption. Therefore, the more thorough proactive SC risk management is implemented, the less a reactive SC Risk Management must be.
TARGUS has a long record of successfully implementing SCRM, and can support you in all phases of integration into your organization; introduction, implementation, and optimization.
Effective Supply Chain Risk Management requires a profound understanding of the intricacies and vulnerabilities of your supply chain. A vulnerability check is a systemic review of your supply chain with the targeted goal of revealing vulnerabilities which have the potential for significant disruption to your operations. The typical results of a Vulnerability Check have been described as, “eye opening”.
TARGUS has SCRM experts that can provide a rapid and detailed analysis of your supply chain vulnerabilities.
Preventive Supply Chain Risk Management works to position your SC to be as prepared as possible for future risk. Building a robust supplier chain to stand against external influences, and can react quickly and flexibly to changing conditions. The more pervasive Preventive Supply Chain Risk Management is in your organziation, the less impact a single events can have on your operations. SCRM is an investment in your company’s future on behalf of your customers and stakeholders, the value of which is difficult to quantify and is often underestimated.
The two elements of Preventive Supply Chain Risk Management are:
Detailed Risk Evaluation
The vulnerability check starts by closely examining the known weaknesses of your supply chain.. This can be, for example, the procurement security of critical components along the entire supply chain. If required, the analysis can covers the entire value chain, starting with the raw materials, through to your consumers. At the end of the analysis possible causes of failure, the supply chain structure, and dependencies within the supply chain are analyzed and made transparent.
The result of the risk evaluation is a risk map, including a quantitative assessment of that risk. Providing a prioritization of the risks to countermeasure and recommendations to counter those risks.
Typical results of risk evaluation:
- Schwachstellen identifiziert
- Risk drivers evaluated
- Gesamtrisiko für das Unternehmen quantifiziert
Präventive Risikominimierung
Die präventive Risikoreduktion greift das Ergebnis der Risikoevaluation auf und bestimmt den Umgang mit identifizierten Risiken. Optionen zum Umgang mit den Risiken sind:
- Eliminieren,
- Minimieren,
- Transferieren (z. B. an Dritte) oder
- Akzeptieren
Aus unternehmerischer Perspektive wird hier sowohl für individuelle Risiken als auch für das Gesamtrisiko eines Unternehmens der optimale Weg bestimmt. Eine ausgeplante Umsetzungsroadmap sowie Regelroutinen stellen den langfristigen Erfolg sicher.
Typische Ergebnisse der Risikominimierung:
- Umgang mit Risiken definiert
- Roadmap zur Mitigation entwickelt
- Routinen implementiert
- Weitere Umsetzung begleitet (bei Bedarf)
Reactive Supply Chain Risk Management involves managing disruptions and the additional risk created after an unexpected event has occurred. Effective preventive risk management will reduce the frequency of disruption and amount of effort needed to support your reactive risk management. When you can’t control all risk, effective reactive risk management becomes a necessary proficiency to avert or mitigate further disruption. The key to successful reactive SCRM is detailed planning of effective of measures and rapid implementation.
Die beiden Hauptelemente des reaktiven Supply Chain Risikomanagements sind:
Supply Chain Stresstest
Der Supply Chain Stresstest analysiert ausgehend von einem aktuellen Ereignis bzw. Störung der Supply Chain die Veränderungen entlang dieser. In drei Schritten werden die Kundennachfrage, Materialversorgung und Auswirkungen auf das eigene Unternehmen analysiert. Als Ergebnis der Analyse steht ein Fahrplan, um trotz möglicher oder erwarteter Unwägbarkeiten das aktuelle Geschäftsjahr bestmöglich abzuschließen.
Weitere Informationen zum Supply Chain Stresstest (LINK)
Typische Ergebnisse des Supply Chain Stresstests:
- Chancen und Risiken aufgrund von Änderungen auf Markt- und Zulieferseite bewertet
- Handlungsempfehlungen zur Sicherung des aktuellen Geschäftsjahres definiert
Krisenmanagement – Lieferanten-Task Force
Das Krisenmanagement ist die passgenaue Lösung bei akuten Störungen der Supply Chain. An erster Stelle steht hier das Schaffen von Transparenz, um die tatsächliche Ursache von Veränderungen zu identifizieren und messbar zu machen. Anschließend erfolgen die Lösungskonzeption sowie eine schnelle und pragmatische Umsetzung. Ein Mittel ist beispielsweise eine Task Force unmittelbar bei einem kritischen Lieferanten zur kurzfristigen Sicherung der Materialversorgung.
Typische Ergebnisse der Lieferanten-Task Force:
- Sofortige Transparenz der Situation geschaffen
- Kurzfristige Lieferfähigkeit sichergestellt
- Schnelle praktische Problemlösung vor Ort


